Are you an investor, student, or finance enthusiast looking to understand how money truly grows over time? If so, you’ve probably come across the term CAGR and wondered what it really means. In today’s fast-paced financial world, knowing just the starting and ending values of an investment isn’t enough—you need a metric that tells the real story of growth.
Welcome! In this guide, we’ll break down the CAGR full form—Compound Annual Growth Rate—in simple, actionable terms. By the end, you’ll not only know how to calculate it but also how to use it to make smarter investment decisions, evaluate business performance, and plan your financial future. Whether you’re tracking your mutual funds, analyzing company revenue, or learning finance for the first time, this article is your ultimate roadmap to mastering CAGR.
What is CAGR? Full Form and Definition
CAGR stands for Compound Annual Growth Rate. It is a financial metric that indicates the mean annual growth rate of an investment or business metric over a specified period of time, assuming the investment grows at a steady rate. Unlike simple growth calculations, CAGR accounts for compounding, giving a smooth, realistic rate of return.
💡 Simple Explanation: If your investment grows unevenly over time, CAGR helps you understand what the annual growth rate would have been if the growth were smooth and consistent.
Why CAGR Matters
CAGR is more than just a number—it is a powerful tool for decision-making in finance and business. Here’s why it is essential:
- Simplifies Growth Analysis
CAGR smooths out fluctuations in growth, providing a clear picture of an investment or business metric over time. - Helps Compare Investments
Comparing two investments or business metrics over several years can be challenging. CAGR provides a standardized annual growth rate to make comparisons meaningful. - Predicts Future Growth
By understanding historical CAGR, investors and analysts can project future performance realistically. - Supports Financial Planning
CAGR can guide personal finance decisions, corporate planning, and strategic business choices. - Eliminates Short-Term Noise
Unlike raw annual returns that fluctuate widely, CAGR provides a more stable and reliable measure.
CAGR Formula Explained
![]()
Where:
- Ending Value (EV): The value of the investment at the end of the period
- Beginning Value (BV): The value of the investment at the start
- Number of Years (N): Duration of the investment or metric
This formula assumes that growth compounds annually, providing a consistent rate of return.
Step-by-Step Example of CAGR Calculation
Let’s say you invested $10,000 in a mutual fund in 2020, and by 2025 it grew to $18,000. To calculate CAGR:
- Identify values:
- Beginning Value (BV) = 10,000
- Ending Value (EV) = 18,000
- Number of Years (N) = 5
- Apply formula:
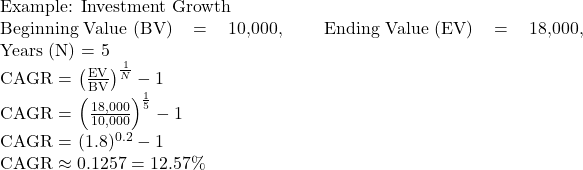
Interpretation: Your investment grew at an average annual rate of 12.57%, even if actual yearly returns varied.
CAGR vs. Simple Growth Rate
Understanding the difference between CAGR and simple growth rate is crucial:
| Metric | Formula | Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Growth Rate | (EV – BV) / BV | Short-term analysis | Easy to calculate | Ignores compounding |
| CAGR | ((EV/BV)^(1/N)) – 1 | Long-term growth | Accounts for compounding, smooths growth | Slightly more complex |
Example:
- Investment grew from $5,000 to $8,000 in 5 years.
- Simple growth = (8,000 – 5,000)/5,000 = 60%
- CAGR = (8,000 / 5,000)^(1/5) – 1 ≈ 9.86% per year
Notice how CAGR gives a more realistic annual growth rate.
How CAGR is Used in Different Fields
CAGR is a versatile metric used across various domains:
1. Stock Market Investments
Investors use CAGR to analyze stock growth over multiple years. It helps compare stocks with different growth patterns to find stable, long-term performers.
2. Mutual Funds
Mutual fund performance reports often show CAGR to indicate how a fund has grown annually, smoothing out market volatility.
3. Business Revenue & Profit Growth
Companies use CAGR to measure revenue, profit, or customer growth. It helps identify trends and plan for future growth.
4. Marketing Metrics
CAGR is used to measure user base growth, sales, or website traffic over time.
5. Economic Analysis
Economists use CAGR to track GDP growth, sector growth, and other macroeconomic indicators over multiple years.
Real-Life CAGR Examples
Here are a few practical examples to understand CAGR better:
Example 1: Business Revenue
![]()
![]()
![]()
Example 2: Stock Investment
![]()
![]()
![]()
These examples show how CAGR simplifies growth analysis across different scenarios.
Tables and Charts: Visualizing CAGR
Table 1: Investment Growth Over 5 Years
| Year | Investment Value ($) |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 10,000 |
| 2021 | 11,200 |
| 2022 | 12,500 |
| 2023 | 14,000 |
| 2024 | 16,000 |
| 2025 | 18,000 |
Chart: Imagine a smooth upward curve representing 12.57% CAGR, compared to fluctuating yearly returns. This visualization shows how CAGR smooths out volatility.
Advantages of CAGR
- Standardized Growth Measure: Provides a single number for comparison.
- Handles Volatility: Smooths irregular growth patterns.
- Forecasting Tool: Helps project future values and plan finances.
- Easy Comparison: Allows comparison of investments with different durations.
Limitations of CAGR
- Does Not Show Yearly Variations: Actual returns may fluctuate widely.
- Assumes Compounding: May be misleading if growth is irregular.
- Not a Complete Performance Indicator: Does not account for risk, inflation, or dividends unless included.
FAQs About CAGR Full Form
1. What does CAGR stand for?
Answer: Compound Annual Growth Rate, representing the smoothed annual growth rate of an investment.
2. How is CAGR different from ROI?
Answer: ROI measures total return, CAGR measures annual growth accounting for compounding.
3. Can CAGR be negative?
Answer: Yes, if the ending value is lower than the starting value.
4. How do I calculate CAGR in Excel?
Answer:
![]()
5. Is CAGR affected by inflation?
Answer: No, but you can calculate real CAGR to adjust for inflation.
6. Can CAGR be used for short-term investments?
Answer: Technically yes, but it’s more meaningful over multiple years.
7. Should dividends be included in CAGR calculations?
Answer: Yes, if you want an accurate representation of total growth.
8. Can CAGR exceed actual annual returns?
Answer: CAGR smooths the rate, so individual years may be higher or lower.
9. Is CAGR widely used in business analysis?
Answer: Absolutely, for revenue, profit, and market growth analysis.
10. How does CAGR help in investment decisions?
Answer: It helps compare growth rates of multiple investments and plan long-term strategies.
Practical Tips for Using CAGR
- Use CAGR to compare mutual funds or stocks over 3–10 years.
- For businesses, calculate CAGR of revenue and profit to assess growth trends.
- Adjust CAGR for inflation to calculate real returns.
- Always combine CAGR with other metrics like volatility, risk, and ROI for a complete view.
CAGR in 2025: Trends and Insights
With financial markets evolving rapidly in 2025, CAGR is more important than ever:
- Stock Markets: Long-term CAGR is used to evaluate tech, healthcare, and emerging market stocks.
- Cryptocurrency Investments: CAGR helps assess the growth of volatile assets over multiple years.
- Mutual Funds & ETFs: Investors increasingly rely on CAGR to compare fund performance.
- Business Planning: Startups and SMEs calculate CAGR for revenue projections and investor presentations.
Conclusion
Understanding the CAGR full form—Compound Annual Growth Rate—is essential for anyone dealing with investments, business metrics, or financial planning. CAGR provides a standardized, reliable, and clear view of growth over time, smoothing out short-term volatility and allowing for better comparison and forecasting.
Whether you are a student learning finance, an investor tracking mutual funds, or a business analyst analyzing revenue, mastering CAGR is a step toward smarter financial decisions. Start applying CAGR calculations today to understand your investments and business growth like a professional.



